
The transition from 2D AutoCAD drawings to Building Information Modeling (BIM) in Revit represents a transformative shift in architectural, engineering, and construction (AEC) workflows. This process not only modernizes design approaches but also unlocks opportunities for greater efficiency, accuracy, and collaboration across project stakeholders.
Why Transition from 2D to BIM?
Traditional 2D AutoCAD drawings have long been a cornerstone of design documentation. However, they lack the depth and functionality that BIM offers. BIM enables a data-rich, 3D modeling environment that integrates geometry, spatial relationships, and comprehensive metadata about building components. This dynamic system helps address the limitations of 2D drafting, such as difficulties in detecting clashes, inefficient workflows, and challenges in visualization.
Benefits of Converting 2D Drawings to Revit BIM Models
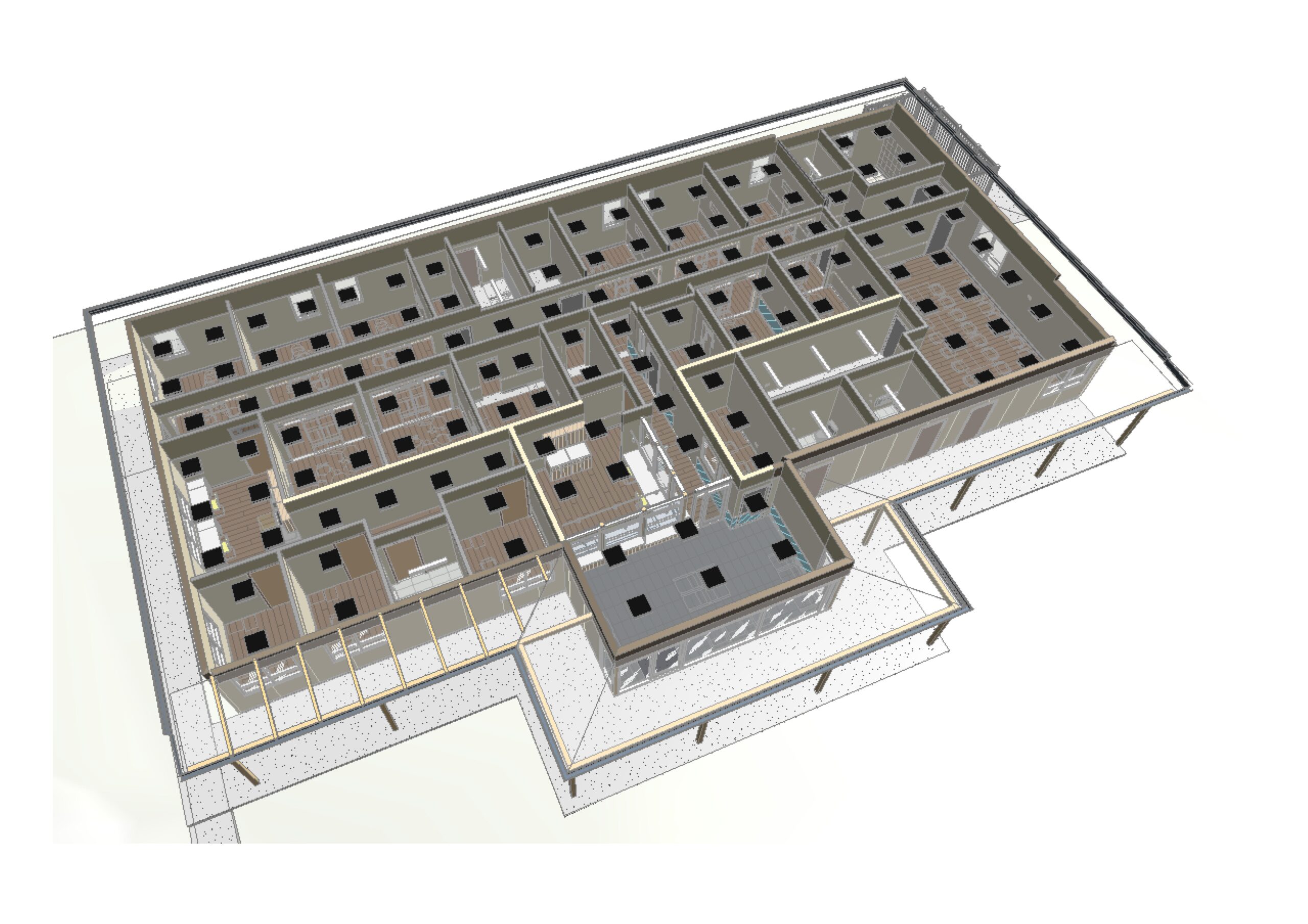
- Enhanced Visualization: Converting 2D AutoCAD drawings into BIM in Revit brings designs to life with detailed 3D models. These models provide stakeholders with a realistic representation of the project, aiding better understanding and decision-making.
- Accurate Documentation: Revit’s parametric modeling ensures that every element in the BIM model is interrelated. Updates to one aspect of the design automatically reflect across associated plans, sections, and elevations, eliminating inconsistencies common in 2D drawings.
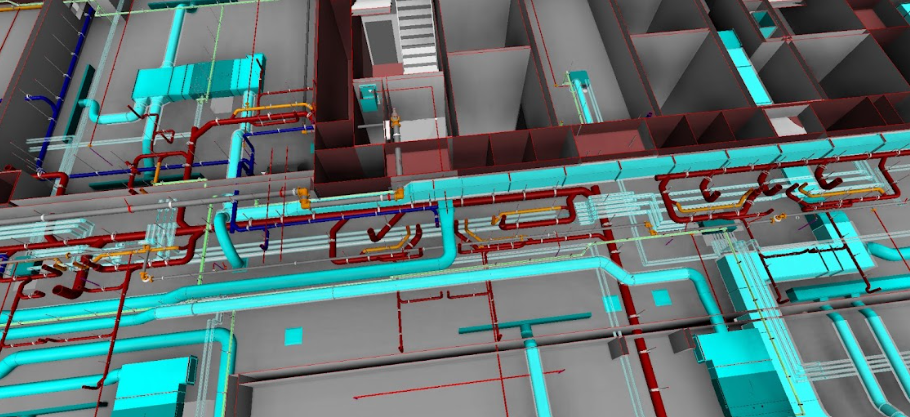
- Clash Detection and Coordination: BIM models facilitate effective clash detection by identifying and resolving design conflicts early in the process, ensuring seamless coordination between architectural, structural, and MEP disciplines.
- Data Integration and Analysis: Beyond geometric modeling, BIM integrates essential project data, enabling simulations, cost estimation, and lifecycle analysis that 2D drawings cannot provide.
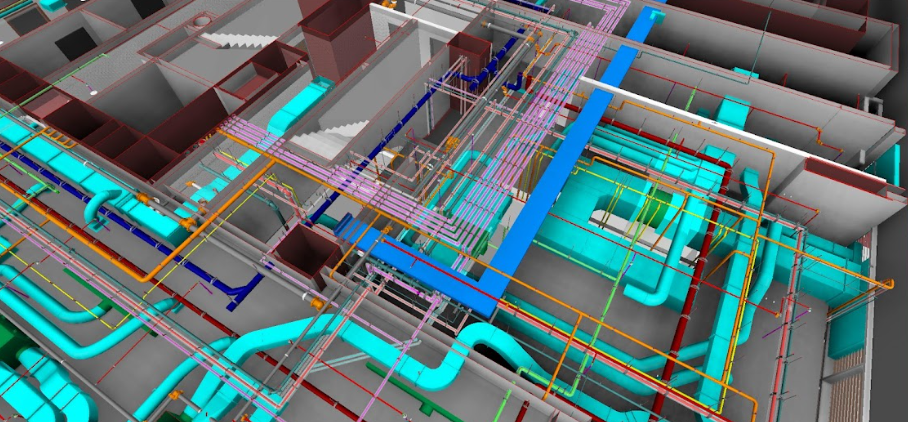


Steps to Convert 2D AutoCAD Drawings to BIM in Revit
- Importing 2D AutoCAD Files: Revit allows users to import DWG files directly. These files can be used as references or templates for developing BIM models.
- Setting Up Grids and Levels: Establishing accurate grids and levels is crucial as they form the framework for the 3D BIM model.
- Creating Parametric Components: Using Revit’s families, users can develop parametric components that correspond to elements in the 2D drawings, such as walls, doors, windows, and more.
- Adding Metadata: The power of BIM lies in its data-rich environment. Populate the model with relevant information about materials, dimensions, and performance characteristics.
- Validating and Coordinating Models: Ensure the model adheres to project standards and integrates seamlessly with other discipline-specific models.


